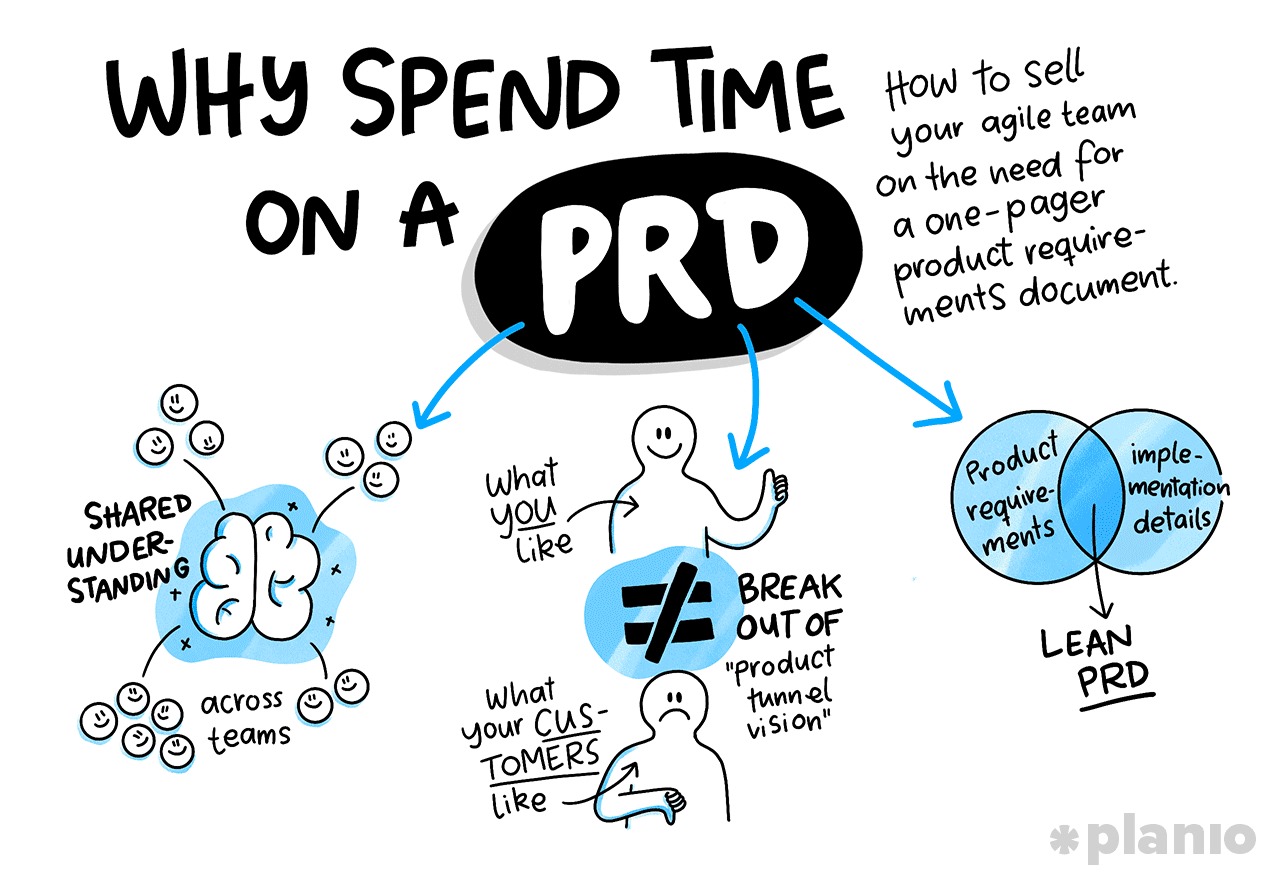
Facing challenges in meeting your customers’ requirements and delivering ideal products that suit their needs? An Effective Product Requirements Documents (PRD) is important for any product development prospect. A PRD makes sure all stakeholders agree and that the product fulfills customers’ needs. This blog post will help you explore what a PRD is, the benefits of drafting a PRD; , product requirements document examples, best practices and a comprehensive guide to create a PRD.
What Is a Product Requirements Document (PRD)?
A PRD provides details about the features and functionality required for a specific product release. It serves as an important reference for the team involved in developing and designing the product. Typically,in waterfall methodology, PRDs are equally significant in Agile product management.
Several other documents can be derived from the PRD:
- Technical Requirements Document: Drafted by engineering teams to provide comprehensive product specifications and system requirements.
- Functional Requirements Document: Created by corporate analysts to describe how users interact with the system.
- User Interface Requirements Document: Drafted by UX designers to describe the product’s design and feel.
Drafting a PRD at the initial stages of the product development process is crucial. Once users’ needs are identified, the PRD should be created to share the exact capabilities required for the product release.
PRD vs. MRD
PRD is quite different from MRD. An MRD provides details about market requirements and customer demands for the product and support business for its development. MRD is created before the Product requirement document to assist in jotting down the capabilities described in the PRD. MRD includes target market details, highlights customers requirements and suggests a timeframe for the launch of the product.
How PRDs Foster Alignment and Success
- Bringing Everyone on Board: A well developed PRD acts as a document that brings everyone on board, it has clear details about the delivery, assumptions, approval criteria, and the release timeline. This document is an evidence of agreement of all the stakeholders and prevents misunderstanding.
- Stay on Track: Identifying the outdated details is important for the development of new products. This assists developers to manage time and cost effectively, preventing frequent changes, which are common pitfalls of product disaster.
- Bridging Gaps: PRD serves as a proof that multiple teams agreed on product viability after exploring market and customer demands. Drafting PRD requires cooperation and communication. Business analysis and UX team provide usability features while the engineering team makes sure technical infrastructure supports the product design.
- Creating Value Through Customer Focus: The essential element of PRD is to prioritize customers’ perspective by incorporating input from the MRD to list down core features and functionality credentials to users. This verifies that the product is well represented, with detailed features and proper time frame for its development.

What Should a PRD Contain?
- Document Metadata: It assists in tracking and storage of a document.
- Product Objectives: It defines the goals which could be achieved in the development of a specific product.
- Customer Research: It often links to MRD which includes customer or market requirements that might impact product development.
- Features: It contains a list of features, capabilities and functionality. In Agile development, this section might include user stories and UX design notes.
- Negative Scope: Details features or functionality that must not be developed in the release.
- System and Environment Requirements: Engineering input describes any system and environment needs.
- Assumptions, Obstacles, and Dependencies: List any hypotheses, obstacles, and dependencies that might influence the product development process.
- Release Criteria: Identify the specific acceptance criteria under which the product is ready for release, including functionality, Utility, reliability, performance, and longevity.
- Success Metrics: Describe metrics if the product is thriving, such as user interaction frequency with a specific feature.
- Timeline: Comprehensive details of the target release date, giving some flexibility for adopting alternative requirements.
Best Practices for PRDs
- Discuss with the Stakeholders: keep all the stakeholders in loop for clarity and highlight any assumptions or obstacles to amend it then and there.
- Ready for any change: PRD must be a living document ready to adopt any modification throughout the product development process to depict customer or market requirements.
- Use Version Control: Maintain a record about original and changed details, assuring appropriate access to all levels.
- Keep It Accessible: The PRD should be visible to the entire team and used as a reference document through the process. Make sure it is stored centrally and that everyone can access and update it.
Steps to Create a PRD
- Be Clear about the Problem: Before drafting PRD the problem should be clear with concrete solutions for it. This will impact the features and functionality included in the product.
- Complete Market and User Research: Evaluate MRD to shape the capability of the product. It provides all the clues for the UX design and business analysis team and impact release time.
- Engage Functional Stakeholders: While creating PRD gather all the stakeholders to collect and address the risk and assumptions or potential obstacles.
- Draft the PRD: Input the customer needs in the product features, decide release criteria and success metrics, highlight time of sprints and milestones to be achieved. Share the draft for review with the stakeholders and modify according to feedback.
- Secure Sign-off: Get sign-off from the customer or project sponsor to ensure business alignment and support. This will assist in preventing misunderstandings about the product’s features, functionality, and performance at the end of the development process.
- Share and Communicate: Store PRD centally and keep communicating the change. Ensure that modifications are highlighted.
In the Product development process the PRD plays a crucial role for assisting teams through each stage and finalizing a dream product which serves as blueprint of success.
Product requirements document examples are an E-commerce website, a mobile fitness App or a Saas project management tool that describe PRD’s importance in defining concrete objectives, features and functionality. By keeping in loop all the stakeholders, going through a detailed market and customer research and focusing on enhancing user experience, the success matrix can be achieved.
And, you can also consider our product development service as well, where our dedicated team guides you seamlessly from initial concept through prototype testing, manufacturing, and logistics, ensuring your vision becomes a successful reality.
Conclusion
Crafting a PRD is time taking but outcomes are invaluable. A clear, aligned document verifies all stakeholders are on the same page and that the product fulfills user needs and demands. Engaginging stakeholders are needed and by following the guideline discussed above you will pave the way to develop a comprehensive and effective PRD that thrives product development.