Your business struggles to control expenditures, and you want to enhance profit margins. A business managing manufacturing production requires comprehensive knowledge of the manufacturing overhead cost formula because this knowledge helps control expenses while boosting profitability.
This article explains manufacturing overhead costs alongside their calculation methods and also emphasizes their significance in business operations. This article provides a complete understanding of manufacturing overhead cost management by teaching calculations for identifying costs and making estimated cost predictions.
What Is Manufacturing Overhead?
The production costs unrelated to direct product tracing form the basis of manufacturing overhead expenses. The determination of manufacturing overhead costs differs from direct costs because it comprises various intangible expenditures, including factory utilities and personnel payments, facility leasing costs, and equipment depreciation.
Understanding the total expenses is crucial in the production process as they contribute to the overall cost structure of a product. To get a deeper understanding of how entrepreneurs can spot opportunities for new products and how they can influence production cost management, check out this insightful article.
Key Elements of Manufacturing Overhead:
- Factory utilities (e.g., electricity, water, heating)
- Indirect labor costs, such as factory supervisors and maintenance workers
- Depreciation of equipment used in the manufacturing process
- Factory rent and maintenance
- Insurance for the factory premises and equipment
- Supplies used in the manufacturing process but not directly incorporated into products
To further align your manufacturing strategy with your business goals and vision, explore Digital Product Strategy and learn how integrating digital tools can reduce unnecessary overhead costs and streamline processes.
Why Is Manufacturing Overhead Important?
Business success depends on precise overhead management because it determines product pricing along with profit calculation and business decision effectiveness.
Here’s why:
- An analysis of overhead expenses through cost tracking enables businesses to recognize wasteful spending as well as enhance operational efficiency.
- A business achieves both market competitiveness and profitable pricing by learning what production costs actually amount to.
- Manufacturing overhead stands as a primary component in determining total manufacturing costs and determining business profit margins.
The Manufacturing Overhead Cost Formula
The manufacturing overhead cost formula is simple and involves adding all indirect production costs. The formula can be expressed as:
Manufacturing Overhead = Indirect Labor + Indirect Materials + Factory Utilities + Depreciation + Other Overhead Costs.
Let’s break this down:
- Indirect Labor: Wages of those employees who are involved in the production line but are not inclined towards manufacturing the product.
- Indirect Materials: Any material that is required in the process of creating any finished goods that is not part of that final product.
- Factory Utilities: Other expenses such as electric power, water, and heating expenses used inside the factory.
- Depreciation: The future predictable expense of depletion of machinery and tools through use.
- Other Overhead Costs: Any further expenses, for example, insurance costs, factory rent, or even maintenance. These costs are usually calculated monthly or annually and are vital for businesses in industries like manufacturing and assembly.
By calculating your manufacturing overhead, you can gain a better overview of your cost structure, which helps you make informed decisions on pricing and investment decisions.
How to Find Manufacturing Overhead Cost
Finding manufacturing overhead includes calculating all indirect costs linked with the production process. These steps are followed to calculate the manufacturing overhead cost.
- Track All Indirect Costs: First of all, one should begin with the consideration of all overhead expenses concerning the production process. Erasmus states that the costs of production also include wages of workers who are not directly involved in the production process, the cost of utilities, and the cost of depreciation of machinery used in the production process.
- Record Costs Periodically: Recording overhead costs at certain intervals is necessary to detect changes and areas of inefficiency when it is early enough.
- Allocate Costs to Products: The costs incurred in the production process from manufacturing overheads are calculated separately; they are then allocated to the product under production. This can be accomplished using various techniques, namely the direct labor hour method or the machine hour method.
- Use the Overhead Rate Formula: The overhead rate formula is also helpful in applying the overhead costs to a specific product. It is calculated as:
Total Manufacturing Overhead = 5000+3000+2000+1000+4000=15000
To find the overhead per unit, divide $ 15,000 by 10,000 units:
Overhead per unit = 15,000 ⁄ 10,000 =1.5 per unit
By multiplying the overhead rate by the direct labor hours or machine hours used by a specific product, you can determine its share of the overhead costs.
Estimated Manufacturing Overhead Cost
Estimating manufacturing overhead costs is important for budgeting and financial forecasting. Overhead cost estimates help in calculating average monthly or annual overhead. Then, anticipated changes are adjusted, such as higher utility costs or new equipment purchases.
How to Estimate Manufacturing Overhead:
- Look at Past Data: Review your historical overhead expenses over a specific period (e.g., the last 12 months) to calculate an average.
- Forecast Changes: If you expect changes in your production process, such as increased production capacity or new machinery, factor those into your estimate.
- Use the Estimated Overhead Rate: The estimated overhead rate is calculated by dividing the estimated total manufacturing overhead by the expected number of direct labor hours or machine hours. This helps you calculate the overhead applied to each.
Key Methods for Allocating Manufacturing Overhead
A report from the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) shows that 60% of companies have transitioned to activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate overhead expenses better. There are several ways to allocate manufacturing overhead costs to products. Here are the most common methods:
1. Direct Labor Hours Method
This is one of the most straightforward methods. They mainly use the direct labor hours to apportion manufacturing overhead costs assigned to the production of a given product. If your factory made 1,000 units, and you have a total effort from workers equal to 5000, 500 labor hours, you divide the total overhead by the direct labor hours to get overhead per unit.
2. Machine Hours Method
This method is usually applied in factories where the usage of the machines is the most significant controlling factor of costs. You spread the manufacturing overheads about the number of hours on the machines employed. The more a particular product may take time to be processed by the machine, the more it will be expected to absorb the overhead costs.
3. Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Another method that is more advanced than ABC is functional-based costing, which allocates overhead based on activities that actually use the resources. There is no way to ignore cost-driving activities such as inspection, setup, or material handling and assign costs appropriately.
Common Challenges in Finding Manufacturing Overhead
Calculating and managing manufacturing overhead can be tricky. Here are some common challenges manufacturers face:
- Accurate Allocation: It can prove analytical to assign overhead costs to products, more so when some of the indirect expenses are spread across products.
- Fluctuating Costs: Essential operating expenses, such as electricity, water, and other expenses, can vary from one period to the other and, hence, are more challenging to predict and control.
- Complex Product Lines: Manufacturing overhead costs of a single product may be difficult to spread when the manufacturer produces many different products or when different products use different amounts of overhead.
How Do You Manage Manufacturing Overhead?
To summarize, finding manufacturing overhead involves identifying all the indirect costs associated with the production process and applying the appropriate allocation method. Whether you use direct labor hours, machine hours, or activity-based costing, the goal is to understand how overhead affects your product’s cost and, ultimately, your profitability.
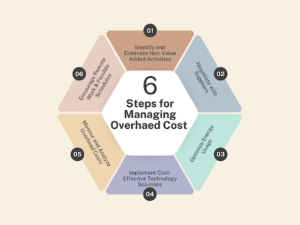
According to a recent survey by Deloitte, 83% of manufacturers reported that managing overhead costs is a key challenge in their operations. To manage overhead costs, businesses need to:
- Identify and Eliminate Non-Value Added Activities
- Implement Cost-Effective Technology Solutions
- Optimize Energy Usage
- Encourage Remote Work and a Flexible Schedule
- Negotiate with Suppliers
- Continuously Monitor and Analyze Overhead Costs
You can make this process easier by using accounting software to track overhead expenses and automatically calculate the overhead rate. Additionally, regularly reviewing your overhead allocation methods will ensure that your costing remains accurate and up-to-date.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing manufacturing overhead is essential for maintaining control over production costs and improving profitability. By mastering the manufacturing overhead cost formula, estimating costs accurately, and selecting the proper allocation methods, you can make informed decisions that positively impact your business’s bottom line.
If you’re facing challenges in managing your manufacturing overhead or need expert support for your manufacturing and sourcing services, Brand New MD™ is here to help. Our team can assist you in streamlining your manufacturing processes and ensuring cost-efficient production, allowing you to focus on growing your business.